cu 2 electron configuration|Electron Configuration of [//substance:Cu2+//] : iloilo Learn how to write the electron configuration for chlorine (Cl) using the .
Cuatro fotos y una palabra 6 letras. Diviértete con el juego que tiene enganchadas a millones de personas. No dejes que ningún nivel detenga tu diversión, aquí tienes la ayuda que necesitas de cuatro fotos y una palabra 6 letras, para seguir jugando.Si te quedas atascado en una palabra ven a 4 Fotos 1 Palabra donde tienes todas las respuestas. .
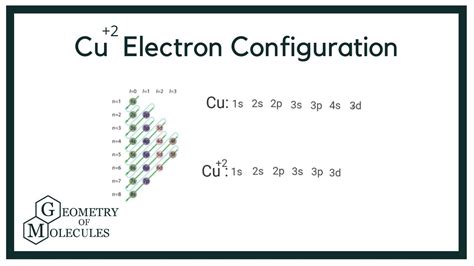
cu 2 electron configuration,How to Write the Electron Configuration for Copper (Cu, Cu+, and Cu2+) In order to write the Copper electron configuration we first need to know the number of electrons for the Cu atom (there are 29 electrons). Once we have the configuration for Cu, the ions are simple.Learn how to write the electron configuration for calcium (Ca) using the .
Learn how to write the electron configuration for magnesium (Mg) using .Learn how to write the electron configuration for potassium (K) using the .cu 2 electron configurationLearn how to write the electron configuration for silicon (Si) using the .cu 2 electron configuration Electron Configuration of [//substance:Cu2+//] Learn how to write the electron configuration for silicon (Si) using the .Learn how to write the electron configuration for chlorine (Cl) using the .
Learn how to write the electron configuration for lithium (Li) using the .
To write the configuration for the Copper ions, first we need to write the electron configuration for just Copper (Cu). We first need to find the number of .Electronic configuration of Cu is 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d9 ([Ar] 4s2, 3d9), whereas for Cu2+ is [Ar], 3d9.
Electron configuration of Cu 2+ is [Ar]3d 9 When copper(II) salts are dissolved in water the blue tetraaquacopper(II) ion or the hexaaquacopper(II) ion is formed. The scope for a .Assuming ion electron configuration | Use full ion electron configuration instead For example, the electron configurations of the transition metals chromium (Cr) and copper (Cu), are not those we would expect. Rather, Cr and Cu take on half . Electronic Configuration of Cu. The electronic configuration of copper (Cu) can be represented as: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10. This configuration indicates that . Electronic configuration of Cu⁺ and Cu²⁺ [duplicate] Ask Question. Asked 1 year, 9 months ago. Modified 1 year, 9 months ago. Viewed 171 times. 0. This question . From Sc on, the 3 d orbitals are actually lower in energy than the 4 s orbital, which means that electrons enter the 3 d orbitals first. In this video, we’ll discuss this in more depth and .The Electron: Crash Course Chemistry #5. Video 2.6.2 2.6. 2: An overview of the role of orbitals in electron configurations and how to write electron configurations. The relative energy of the subshells determine the order in which atomic orbitals are filled (1 s, 2 s, 2 p, 3 s, 3 p, 4 s, 3 d, 4 p, and so on).

In this case, 2+2+6+2+6+2+10+6+2+1= 39 and Z=39, so the answer is correct. A slightly more complicated example is the electron configuration of bismuth (symbolized Bi, with Z = 83). The periodic . The electronic configuration of copper (Cu) can be represented as: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10. This configuration indicates that copper has 29 electrons distributed in its electron shells. The first shell has 2 electrons, the second shell has 8 electrons, the third shell has 18 electrons, and the fourth shell has 1 electron.The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = + 1 2 ).
The electron configuration of copper is : 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10. Cu has a unique fully-filled 3d configuration in its ground state and so has unique physical and chemical properties. It has a typical fcc structure and is reddish brown coinage metal with excellent heat and electrical conductivity. Copper is found abundantly in a variety .The electronic configuration for $\ce{Cu}$, adjusted for Hund's rule, is: . {Cu^{+2}}$ compounds will form. In fact $\ce{Cu^{+2}}$ is the most common oxidation state of copper so the energetics must generally work out that the energy gained by forming more than one bond to copper and gaining additional lattice (or hydration) stabilization . While demonstrating the first step of identifying the number of valence electron in Copper this can be recognised from the electronic configuration that is for Cu is 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104s1. It means the number valence electron in Copper is 9. Next step is to put dots as the notation of electrons around Cu that is 9 dots.
What is The Electron Configuration of Copper. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 is the electron configuration of Cu. If the general pattern of filling electron orbitals is followed, then copper’s electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d9. The only difference is at the end of the configuration that is in the 3d and 4s shells.
Electron Configuration of [//substance:Cu2+//] The electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are: The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. This electron must go into the lowest-energy subshell available, the 3s orbital, giving a 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 configuration. Add an electron to the anion electron configuration. For example, the ground state electronic configuration of chlorine is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁵. For Cl −, it will be 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶. Remove the outermost electrons in the cation, e.g. electron configuration for Mg 2+ will be 1s²2s²2p⁶.
Introduction to electron configurations. Electron configurations describe where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. For example, the electron configuration of .The electronic configuration of cations is assigned by removing electrons first in the outermost p orbital, followed by the s orbital and finally the d orbitals (if any more electrons need to be removed). For instance, the ground state electronic configuration of calcium (Z=20) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2.
The correct option is D [Ar] 3d9 4s0. The atomic number of Cu is 29. Its electronic configuration is. [Ar] 3d10 4s1. When 2 electrons are lost, Cu2+ with electronic configuration [Ar] 3d9 is obtained. Suggest Corrections. An atom's electron configuration describes the way its electrons fill sublevels when the atom is in its ground state. Atoms seek the most stable electron configuration, so sublevels are half-filled or fully-filled .
Video: Cr, Cr2+, and Cr3+ Electron Configuration Notation. In writing the electron configuration for Chromium the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Chromium go in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. In the case of first row transition metals, the electron configuration would simply be [Ar] 4s x 3d x. The energy level, "n", can be determined based on the periodic table, simply by looking at the row number in which the element is in. However, there is an exception for the d-block and f-block, in which the energy level, "n" for the d block is .The electronic configuration of C u (I) is [A r] 3 d 10. The electronic configuration of C u (I I) is [A r] 3 d 9. The stabilities of the ions depend on their hydration energies released when the ions get linked to the water molecules. C u (I I) ion has a smaller size and a greater charge. So, it has a higher charge density compared to C u (I) ion.
cu 2 electron configuration|Electron Configuration of [//substance:Cu2+//]
PH0 · What is the the electron configuration of #Cu^(2+)#?
PH1 · What is Electron Configuration for Cu+2?
PH2 · What is Electron Configuration for Cu+2?
PH3 · How To Write Electron Configuration For Cu
PH4 · Electronic configuration of Cu⁺ and Cu²⁺
PH5 · Electron Configuration of [//substance:Cu2+//]
PH6 · Electron Configuration for Cu, Cu+, and Cu2+ (Copper and
PH7 · Electron Configuration for Cu, Cu+, and Cu2+ (Copper and
PH8 · Electron Configuration for Copper (Cu, Cu+, Cu2+)
PH9 · Electron Configuration for Copper (Cu, Cu+, Cu2+)
PH10 · Cu Electronic Configuration and Distribution in Shells
PH11 · Copper Cu transition metal Chemistry copper (I) Cu+ copper (II)
PH12 · 1.9: Electron Configurations for Transition Metal Elements